3D PAD Electrode: Redefining Next-Generation Batteries
Traditional battery electrodes are usually flat or randomly porous structures, where ion transport relies on uncontrolled pathways, leading to:
- Slow ion diffusion, limiting charge/discharge speed
- Difficulty using thicker electrodes, restricting energy density
- High risk of lithium dendrite formation, causing short circuits
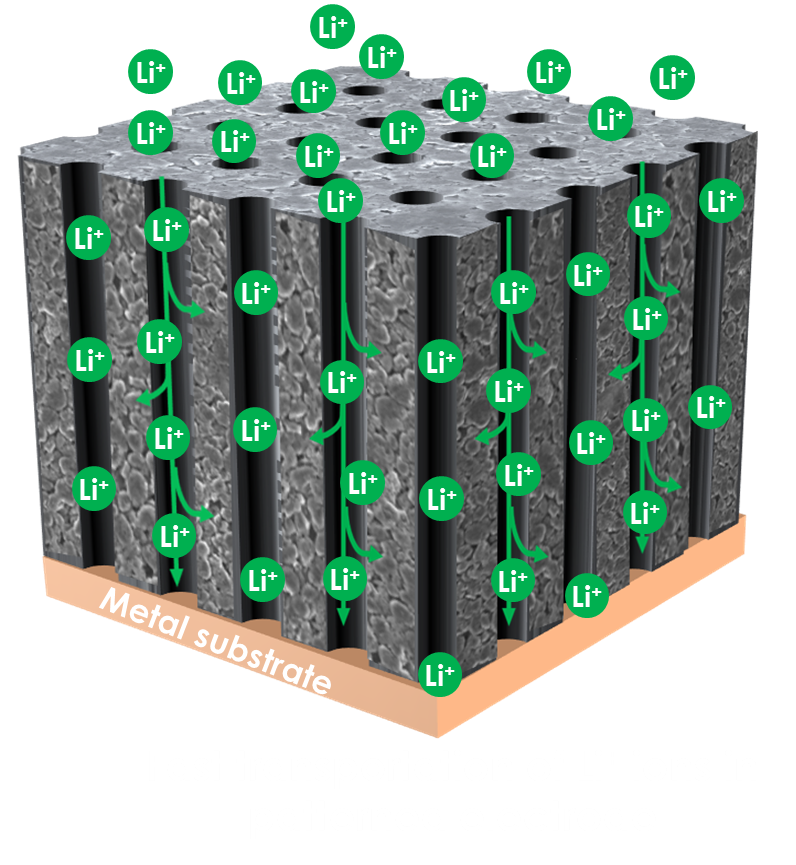
Our 3D PAD (Three-Dimensional Pore Array Diagram) electrodes feature an ordered 3D pore structure, revolutionizing ion transport:
- Fast ion channels: Direct pathways within the electrode for rapid Li⁺ transport
- High energy and power: Supports thicker electrodes for greater energy and power density
- Safe and durable: Effectively suppresses lithium dendrites, reduces short-circuit risk, and extends the lifetime of silicon-doped anodes
- Sustainable manufacturing: Wet and dry screen-printing processes lower production costs and enhance environmental sustainability
The 3D PAD design uniquely combines performance, safety, and sustainability, unlocking unprecedented potential for electric vehicles, drones, robotics, and eVTOLs.
 Si-Anode Longevity
Si-Anode Longevity
Significantly extends the lifetime of silicon-doped anodes.
 Screen Printing Efficiency
Screen Printing Efficiency
Wet and dry roll-to-roll screen printing enables high-precision, scalable, and cost-efficient production.
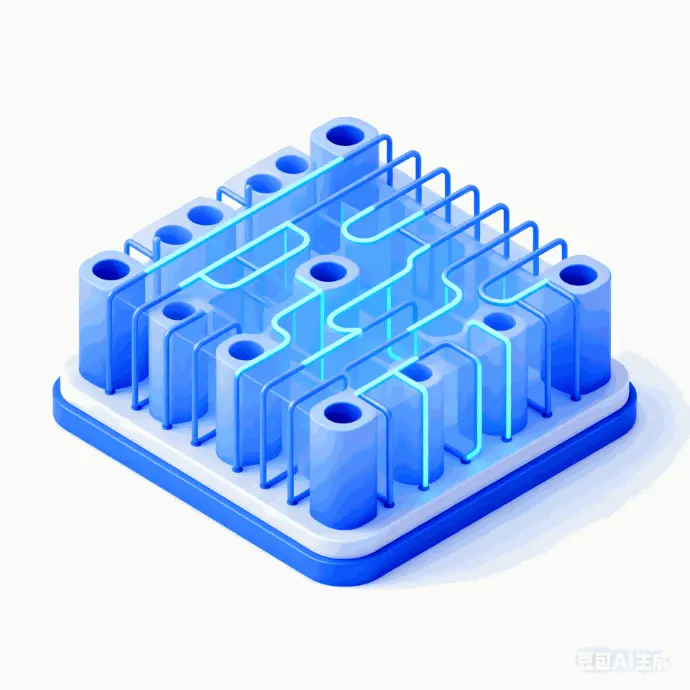 Ordered Pore Channels
Ordered Pore Channels
3D PAD electrodes have aligned pore channels that provide fast pathways for lithium-ion transport.
 Thick Electrode Support
Thick Electrode Support
Enables thicker electrodes for higher energy and power density while minimizing inactive component weight.
 Sustainability & SSB Compatibility
Sustainability & SSB Compatibility Reduces energy consumption, while being compatible with solid-state batteries (SSB).
 Dendrite Suppression
Dendrite Suppression
Prevents lithium dendrite formation, enhancing safety, cycle life, and charge/discharge performance.
Key Mechanism
Thicker electrodes increase areal charge capacity but usually slow ion transport (tradeoff between energy density and power).
XRBT solves this by printing small, highly ordered holes (HOLE technology) into the electrode, ensuring fast Li⁺ transport without compromising thickness.
Outcome
- Achieves high energy density, high power output, long cycle life, and scalable, low-cost manufacturing.
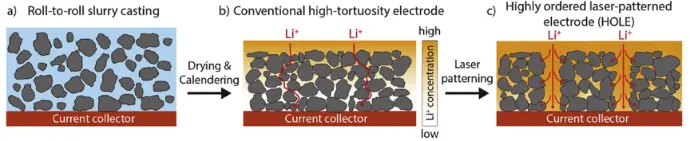
*Reproduced from Chen et al., Efficient fast-charging of lithium-ion batteries enabled by laser-patterned 3D graphite anode architectures, University of Michigan.
Mitigate Dendrite Growth –
Ensuring Safer, Longer-Lasting Batteries
Lithium metal batteries offer high energy density, but uneven lithium deposition can form dendrites—needle-like structures that may pierce the separator and cause short circuits.
Our 3D PAD (3-Dimensional Pore Array Diagram) electrode creates uniform channels for lithium ions, controlling dendrite growth and directing expansion within the electrode. This innovative design reduces short-circuit risk, provides more space for lithium expansion, and ensures safer, longer-lasting battery performance.
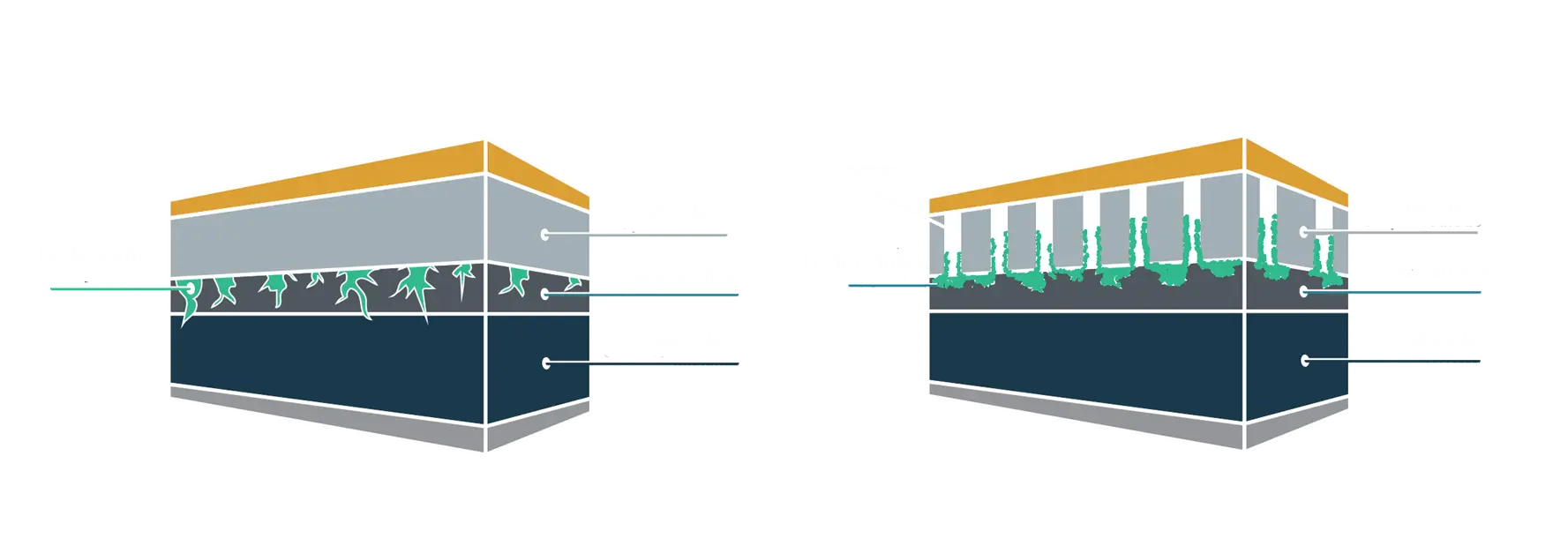
Cost Savings:
XRBT’s 3D PAD technology optimizes electrode design with lowering production costs by minimum -9,2% compared to traditional batteries—delivering higher efficiency and better value without compromising performance. In addition, the thick electrode offers a higher gravimetric and volumetric energy density.
Improvement in Volumetric Energy Density
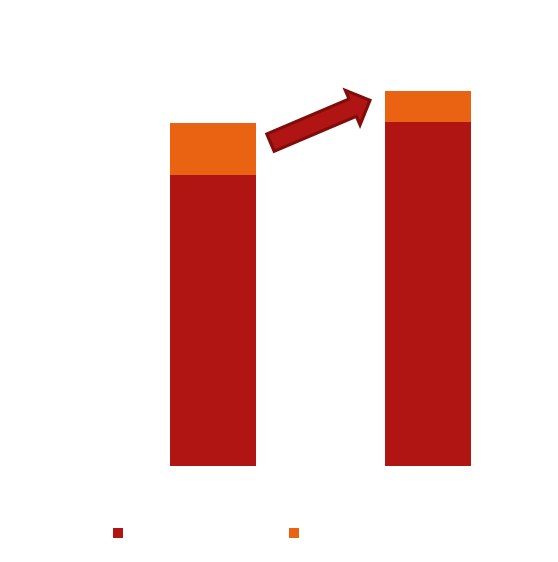
Improvement in Gravimetric Energy Density
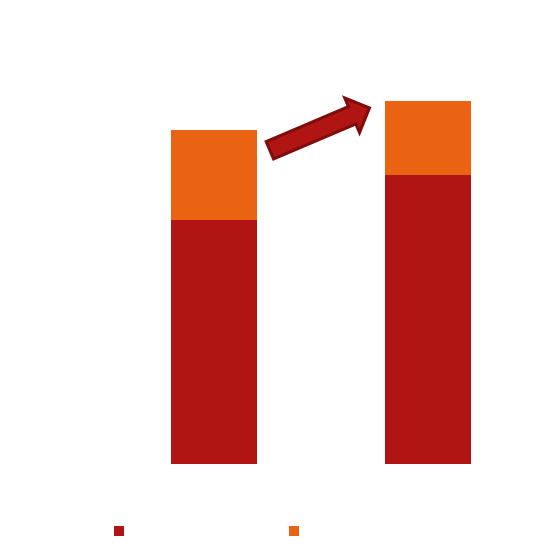
Basis for this calculation: NMC622 Cell, blade format 340 mm x 80 mm, cathode thickness 78 𝜇m -> 156 𝜇m
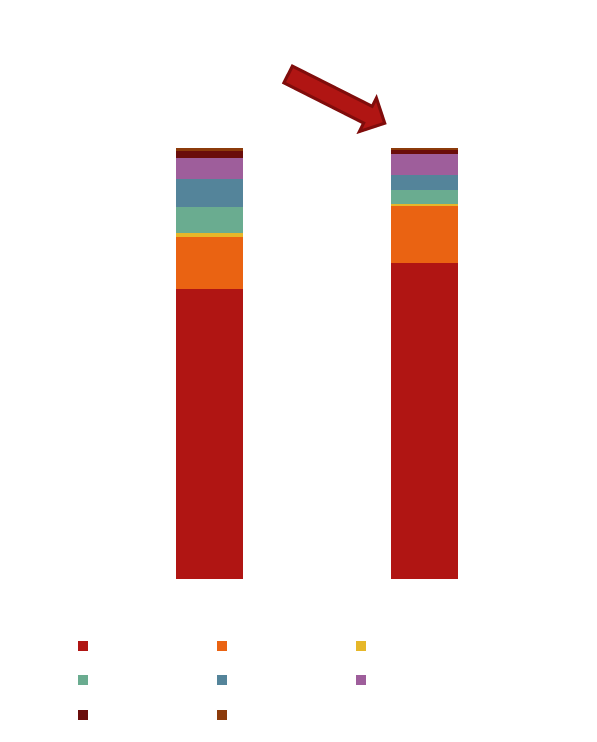
| Traditional Batteries | XRBT 3D PAD Technology |
|---|---|
| Require long drying furnaces (50m+) and dry rooms → energy intensive | Micro-environments + IR drying → faster & energy efficient |
| 100–150 µm thick layers in one step → slow & difficult to dry | ~50 µm thin layers in 3 steps → quick & easy to dry |
| Thick layers risk cracks during drying | Thin porous layers allow solvent to escape easily |
| ~€70–100M capital required per 1 GWh capacity | ~€50M capital required per 1 GWh capacity |
| Slurries with ~75% solvent content | Pastes with ~50% solvent content → less solvent, less energy needed |
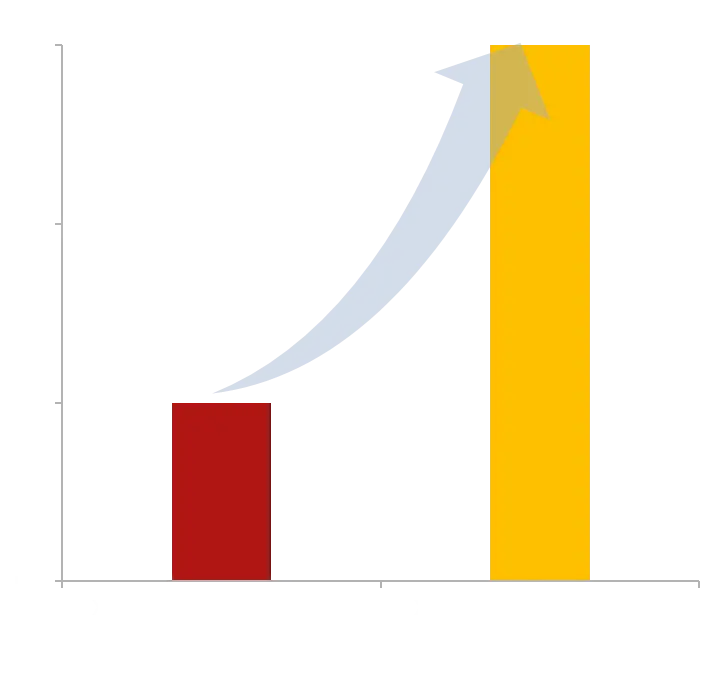
Enhanced Lifetime of Si-Anodes
Higher Capacity:
Silicon stores far more lithium than graphite

Key Challenges:
Expansion, cracks, unstable SEI, reduced cycle life

Our Solution:
3D PAD pores absorb expansion, prevent cracks, stabilize SEI
 Result:
Result:
Longer lifetime & higher efficiency, scientifically validated
Advantages of 3D PAD technology when used in SSB
Solid-state batteries replace liquid electrolytes with solid ones, offering higher safety and greater energy density than conventional lithium-ion cells. However, they are hard to mass-produce due to layer delamination.
Building on XRBT’s dry printing process and 3D PAD electrodes, our technology enables practical solid-state batteries with scalable, high-precision production. Key benefits include:
Layer interlocking without external pressure → avoids delamination during charge/discharge
Efficient, chip-like production → synchronized layer-by-layer fabrication increases throughput and reduces defects
Smooth electrolyte-to-separator transitions → only achievable with printing
Support for high-voltage bipolar cells → prevents internal short circuits via printed arresters and housings
This approach makes SSB production more precise, reliable, and cost-effective, unlocking new possibilities for next-generation energy storage applications.
Advantages
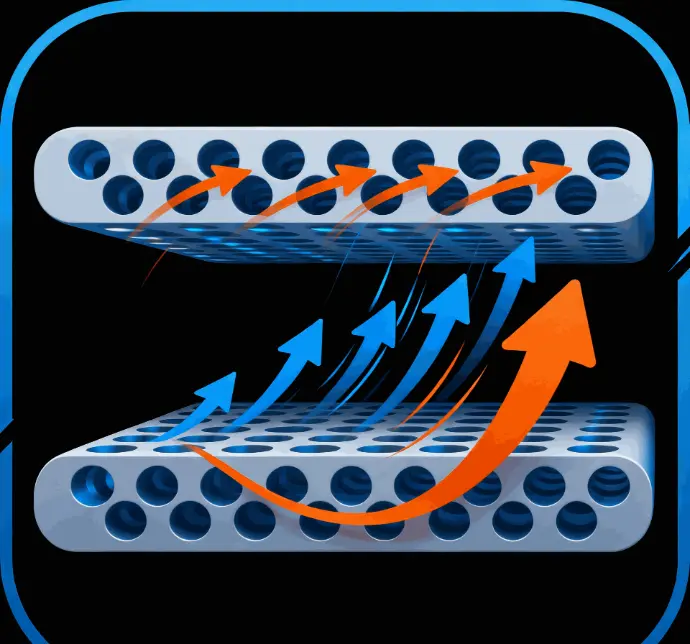
Fast Ion Transport
Ordered pore channels enable rapid lithium-ion movement, improving charge/discharge efficiency.

Thick Electrodes
Supports thicker electrodes for higher energy density.

Dendrite Suppression
Suppresses lithium dendrites, enhancing safety and cycle life.

High Performance
Delivers high energy density, charging/discharging capability , and long cycle life

Cost Efficient
Optimized design reduces manufacturing costs.